39 simple harmonic motion worksheet answers
HyperPhysics - GSU *harmonic oscillator *harmonic oscillator, quantum *heat *heat of fusion *heat of vaporization *heat transfer *helium, liquid *helium-neon laser *Helmholtz free energy *Henry's Law *Hermite polynomials *Hertzsprung-Russell diagram *Heterodyne principle *Higgs boson *Hooke's Law *holography * Hubble constant * Hubble law * hydraulic brakes Graphs of Motion - Practice – The Physics Hypertextbook The third and fourth methods use the other two equations of motion. Since these rely on our choices for the final velocity, multiple valid answers are possible. Let's say we use the velocity calculated from the slope of a "tangent" with a value of −60 m/s and and the velocity-time relationship, a.k.a. the first equation of motion. Then…
2.2 Speed and Velocity - Physics | OpenStax (4) Science concepts. The student knows and applies the laws governing motion in a variety of situations. The student is expected to: (B) describe and analyze motion in one dimension using equations with the concepts of distance, displacement, speed, average velocity, instantaneous velocity, and acceleration.

Simple harmonic motion worksheet answers
Kinematic Equations: Sample Problems and Solutions Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations. Work and Energy Review - with Answers #1 - Physics Classroom g. For uniform circular motion, the force is inwards and the displacement at each instant is tangent to the circle; these two vectors make a 90 degree angle. h. This is a straightforward question; no tricks here. i. The forward motion is do to the forward pushing; if the force and motion are in the same direction, then the angle is 0 degrees. j. Acceleration - Physics Classroom As mentioned earlier in Lesson 1, an object moving in uniform circular motion is moving in a circle with a uniform or constant speed. The velocity vector is constant in magnitude but changing in direction. Because the speed is constant for such a motion, many students have the misconception that there is no acceleration.
Simple harmonic motion worksheet answers. Electric Circuits Review - Answers #2 - Physics Classroom Answer: B. A water ride at a water park is analogous to an electric circuit. First of all, there is an entity which flows - water flows in a water park and (in conventional terms) + charge flows in an electric circuit. Acceleration - Physics Classroom As mentioned earlier in Lesson 1, an object moving in uniform circular motion is moving in a circle with a uniform or constant speed. The velocity vector is constant in magnitude but changing in direction. Because the speed is constant for such a motion, many students have the misconception that there is no acceleration. Work and Energy Review - with Answers #1 - Physics Classroom g. For uniform circular motion, the force is inwards and the displacement at each instant is tangent to the circle; these two vectors make a 90 degree angle. h. This is a straightforward question; no tricks here. i. The forward motion is do to the forward pushing; if the force and motion are in the same direction, then the angle is 0 degrees. j. Kinematic Equations: Sample Problems and Solutions Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations.

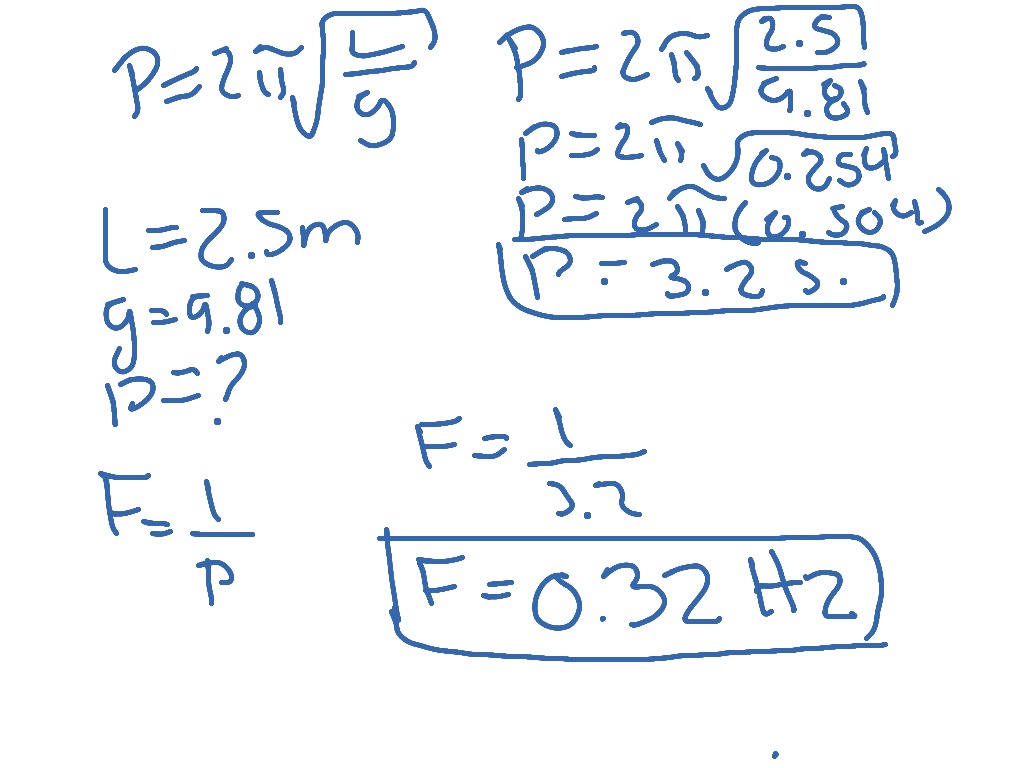
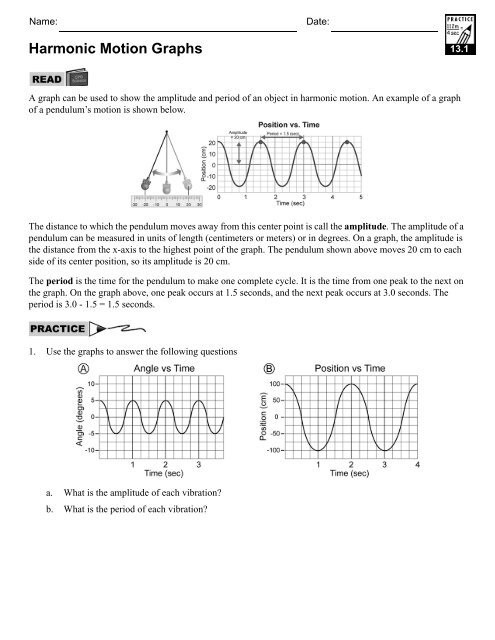













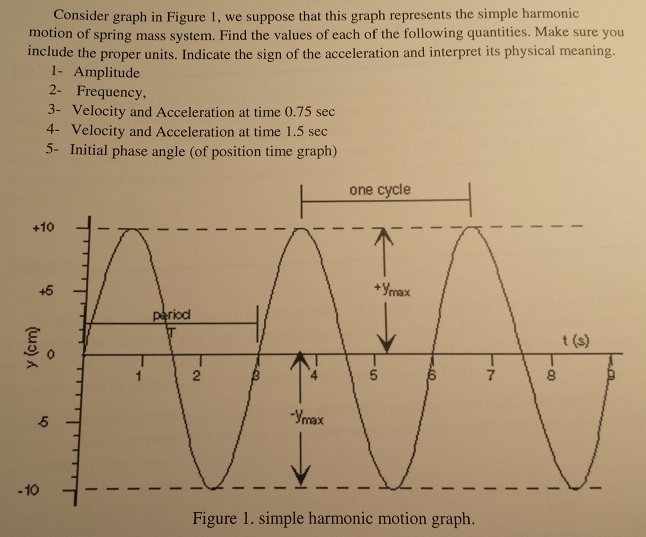





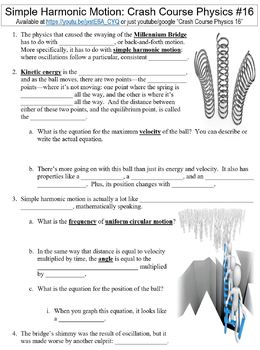





0 Response to "39 simple harmonic motion worksheet answers"
Post a Comment